|
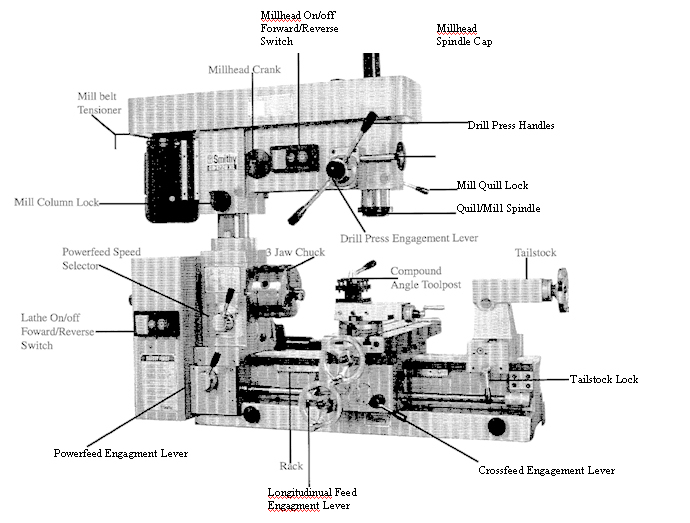
Bed
The bed is the machine's
foundation. It is heavy, strong, and built for absolute
rigidity. The two ways on the top are the tracks on
which the carriage and tailstock travel. To maintain an
exact relationship between toolpoint and workpiece from
one end of the machine to the other, the ways must be
absolutely true and accurately aligned to the line of
centers and to one other.
Carriage
The carriage consists of
the saddle and apron. It moves by hand or power along
the bed, carrying the cross slide, compound rest, and
toolpost. Its function is to support the cutting tool
rigidly and move it along the bed for different
operations. It locks into place by tightening the
carriage lock with the set screw on the back side of the
carriage.
Compound rest
Mounted on the cross
slide, the compound rest swivels to any angle horizontal
to the lathe axis to produce bevels and tapers. Cutting
tools fasten to a toolpost on the compound rest. The
calibrations on the front of the base are numbered in
degrees from 60° right to 60° left.
Cross slide
The T-slotted cross
slide moves crosswise at 90° to the lathe axis by manual
turning of the cross-feed screw handwheel. It also
serves as the milling table.
Drill
press and fine-feed clutch
Pushing in the drill
press clutch (engages the fine feed. To work the clutch,
release the spring tension by rotating the drill press
handles clockwise. Pull the clutch out to use it as a
drill press or push it in to use the fine feed. Use the
fine-feed handwheel to move the quill up and down.
Forward/Off/Reverse switch
This is the main switch
used to operate the lathe. It is simply a
forward/reverse switch for the motor. The motor turns
counterclockwise for normal lathe operation and
clockwise for normal milling and drilling. The CB-1220
XL LTD has two switches, one located on the millhead and
one on the headstock.
Gearbox
The gearbox houses the
belts that drive the spindle and change gears for the
powerfeed. Select the thread pitch (for threading) or
the feed rate (for turning) by changing the four change
gears on the right side of the gearbox.
Headstock
The headstock , which is
secured to the bed, houses the gears that drive the
powerfeed and the taper bearings that secure the lathe
spindle.
Lathe
spindle
The end of the lathe
spindle facing the tailstock ( is the spindle nose. The
spindle nose, which has an MT4 taper, rotates the
workpiece and drives lathe chucks and other workholding
devices. All attachments (three-jaw chuck, four-jaw
chuck, faceplate, etc.) bolt to the spindle flange
either directly or via an adapter plate.
Leadscrew
The leadscrew which runs
the length of the bed, moves the carriage for lathe
turning or thread cutting. It works both manually and
under power. You can also use it manually with
the mill.
Locks
Locks on the cross
slide, carriage, quill, and tailstock (two), keep them
from moving. During machining, lock all axes except the
one you want to move.
Micrometer control and calibration
Just inside the handles
of the tailstock crossfeed, drill calibrated in
millimeters. The compound feed and crossfeed are
calibrated in two thousandths, the tailstock in
thousandths, the leadscrew in two thousandths, and the
drill press in forty thousandths.
These micrometer dial
collars can move independently around the handle shafts.
This independent motion is called float. The CB-1220 XL
LTD has floating dials on the cross slide, tailstock,
longitudinal and mill feeds. They let you zero the
collars at any point and read the feed travel from that
point on the dial for increased accuracy.
Mill
spindle
The mill spindle
attaches to the quill, which moves in and out of the
head. The quill lock keeps the quill still when you
install or remove tools from it and while milling
horizontally. Usually, tools fit into collets that
attach through the spindle via drawbars.
Half-nut lever
This lever transmits
power to the carriage for threading.
Power
Longitudinal-feed
Push the lever down to
engage the power of the long feed for general cutting.
Power
Cross-feed
Push the lever down to
engaged the cross-feed and pull it up to disengage
Powerfeed speed selector
The two-speed selector
for powering the leadscrew is on the front of the
headstock. The leadscrew turns twice as fast in the H
position as in the I position.
Tailstock
The tailstock, which
provides right-end support for the work, moves along the
bed and can stop at any point on it. It holds centers,
drills, reamers, taps, and other tools. To move the
tailstock spindle, which has an MT3 taper, turn the
tailstock handwheel. The scale of offset calibrations on
the back of the tailstock is in millimeters.
To offset the tailstock,
loosen the four base-locking bolts. To offset to the
left, loosen the left adjusting bolt and tighten the
right. To offset to the right, loosen the right
adjusting bolt and tighten the left.
|